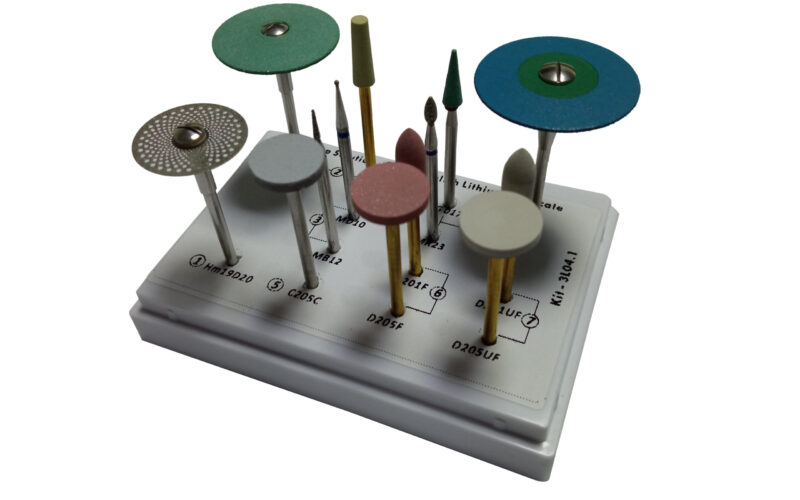
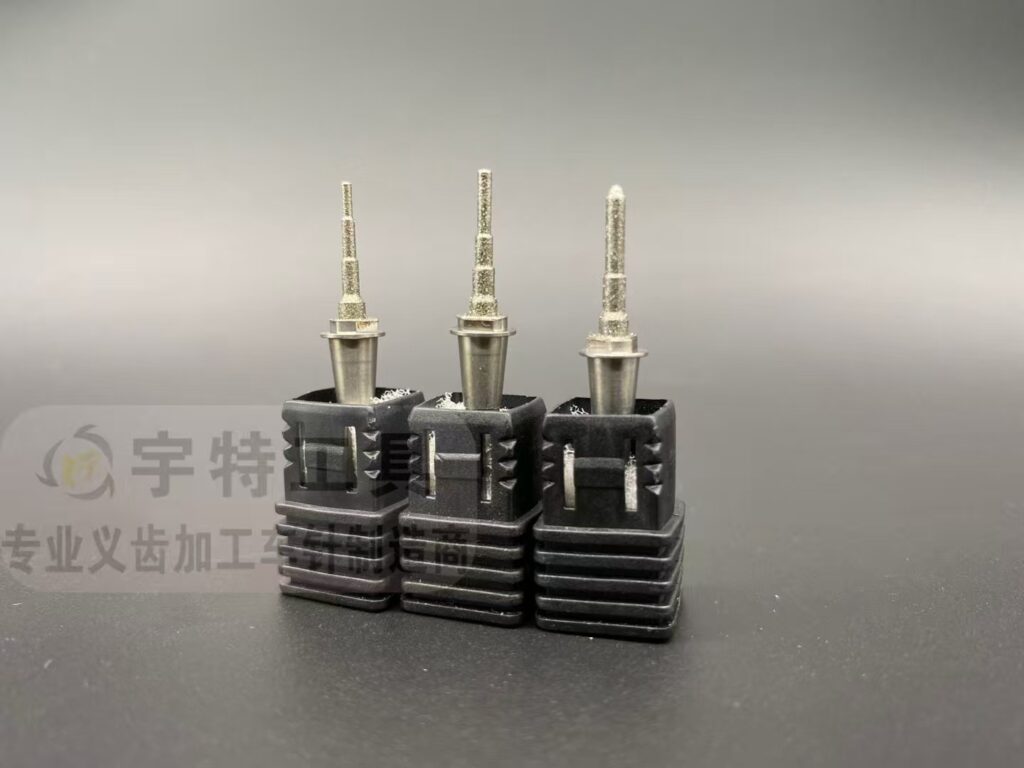
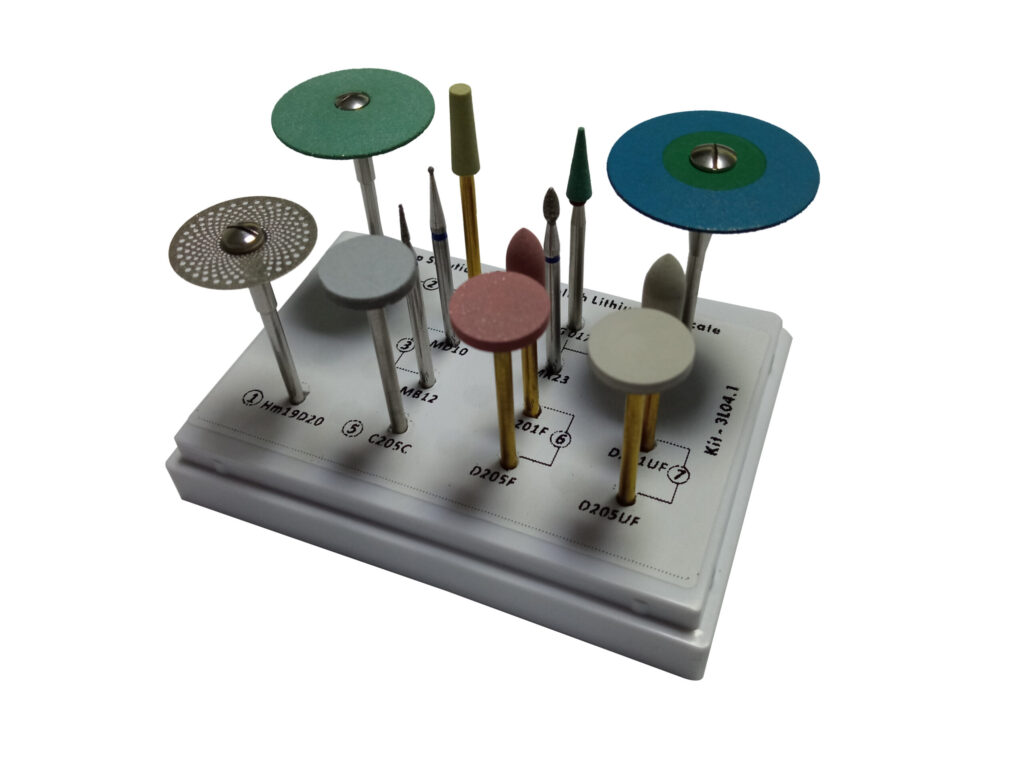
Selecting the right dental lab burs is critical to achieving precise results in prosthodontics, restorations, and custom fabrication. Whether you’re working on crowns, bridges, or advanced materials like zirconia and lithium disilicate, understanding bur types and applications ensures efficiency, longevity, and flawless outcomes. Below, we break down key considerations—including a dedicated guide to CAD/CAM milling burs—to help you optimize your workflow.
Why Bur Selection Matters
Using the wrong bur can lead to tool wear, material damage, or compromised restorations. For example, overheating acrylic with a coarse bur may melt it, while using a dull diamond on zirconia could cause microcracks. By matching burs to materials and tasks, you enhance precision, reduce waste, and protect your tools—and your reputation.
CAD/CAM Milling Burs: Material-Specific Solutions
CAD/CAM technology demands burs optimized for precision, speed, and durability. Here’s a breakdown of material-specific CAD/CAM milling burs:
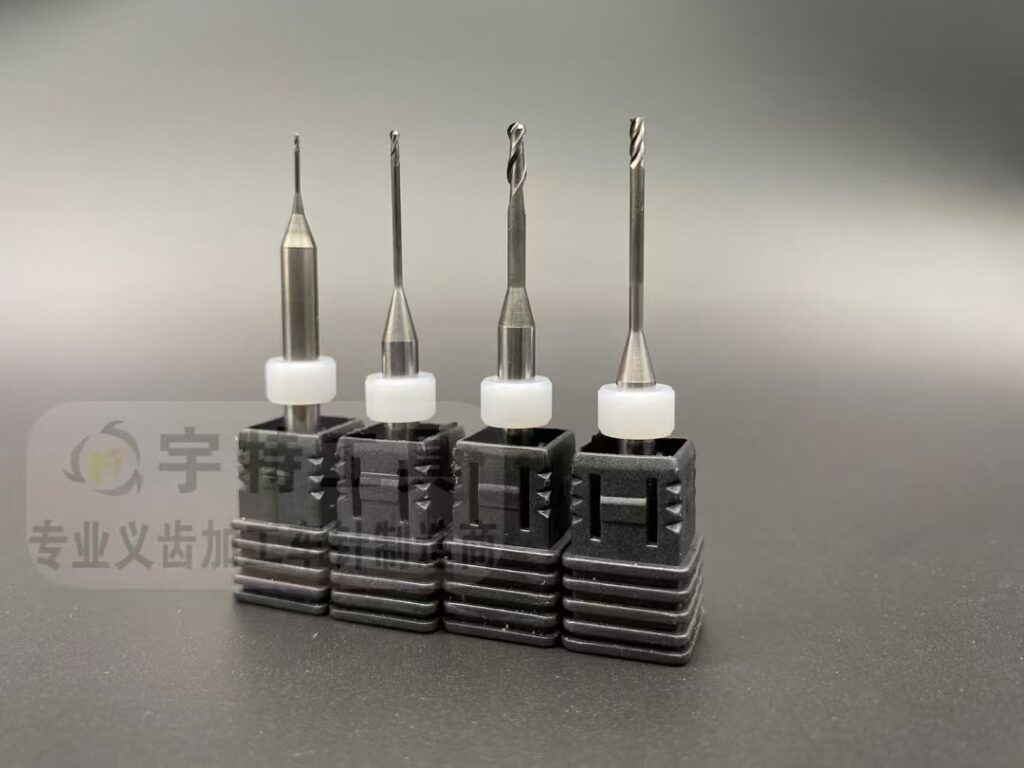
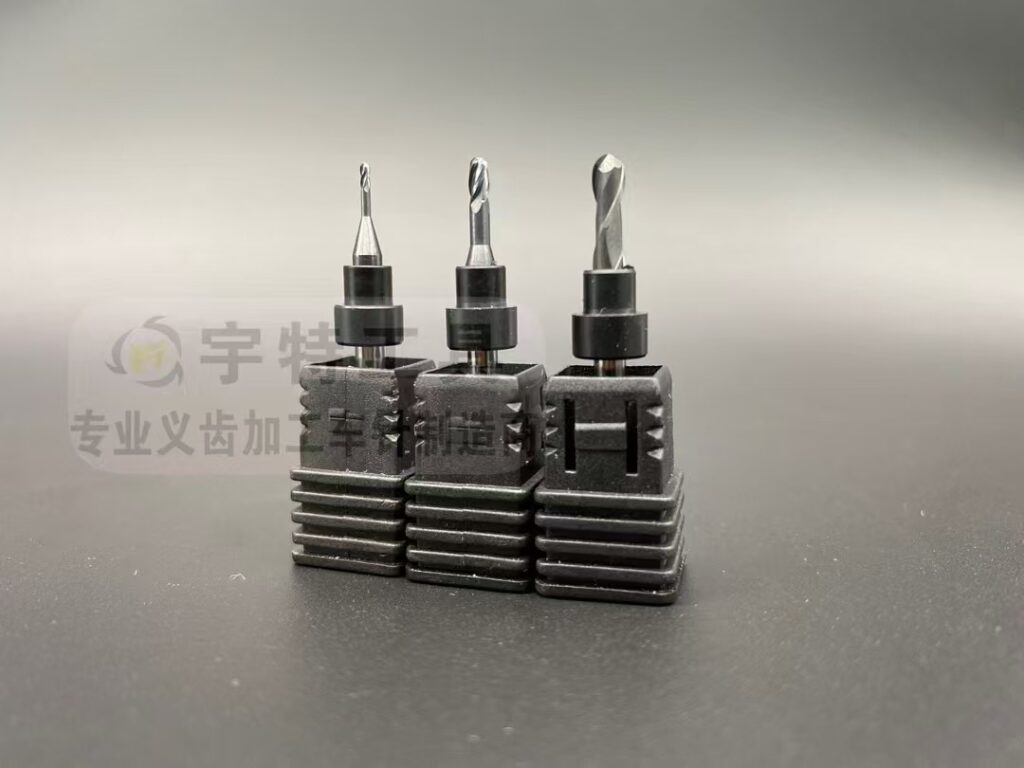
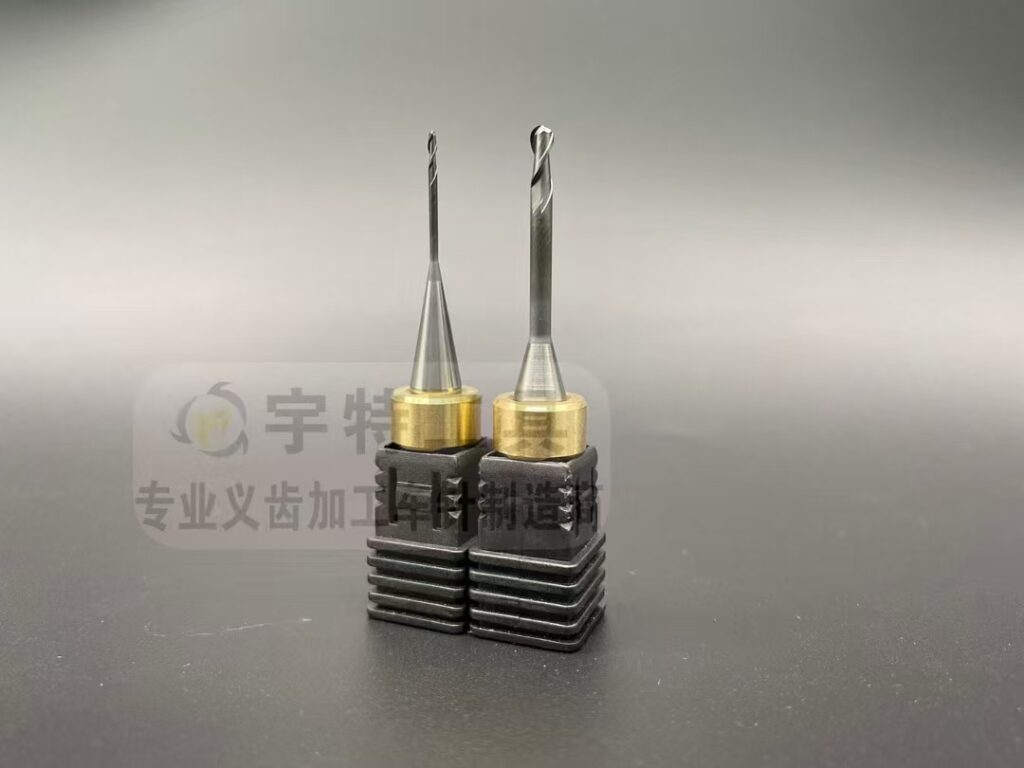




1. Wax (for Impressions & Models)
- Best Burs:
- Carbide burs for heavy shaping.
- Resin-bonded diamond burs for fine details.
- Applications: Trimming wax models, carving intricate margins.
- Tip: Use low speed with air cooling to avoid melting wax.
2. Titanium (for Implants & Frameworks)
- Best Burs:
- Tungsten carbide burs for heavy reduction.
- HSS (high-speed steel) burs for initial contouring.
- Applications: Milling implant abutments, refining titanium bars.
- Tip: Prioritize rigidity; carbide resists wear during high-speed milling.
3. Zirconia (for Strong, Precision-Milled Restorations)
- Best Burs:
- Silicon rubber diamond burs for coarse grinding (prevents chipping).
- Monocrystalline diamond burs for fine details (margins, occlusal adjustments).
- Applications: Milling monolithic crowns, bridges, and implant-retained prostheses.
- Tip: Use light pressure and water cooling to avoid overheating. Ceramic HP burs (zirconia-infused) are ideal for finishing.
4. Lithium Disilicate (e.max®)
- Best Burs:
- Fine-grit resin-bonded diamond burs (minimize chipping).
- Coarse-grit diamonds for initial reduction, followed by polishing wheels.
- Applications: Shaping veneers, crowns, and multi-layered restorations.
- Tip: Avoid dry milling—use water spray to prevent thermal shock.
Traditional Handcrafted Restorations: Bur Guide
For manual or semi-automated tasks, bur selection varies by material:
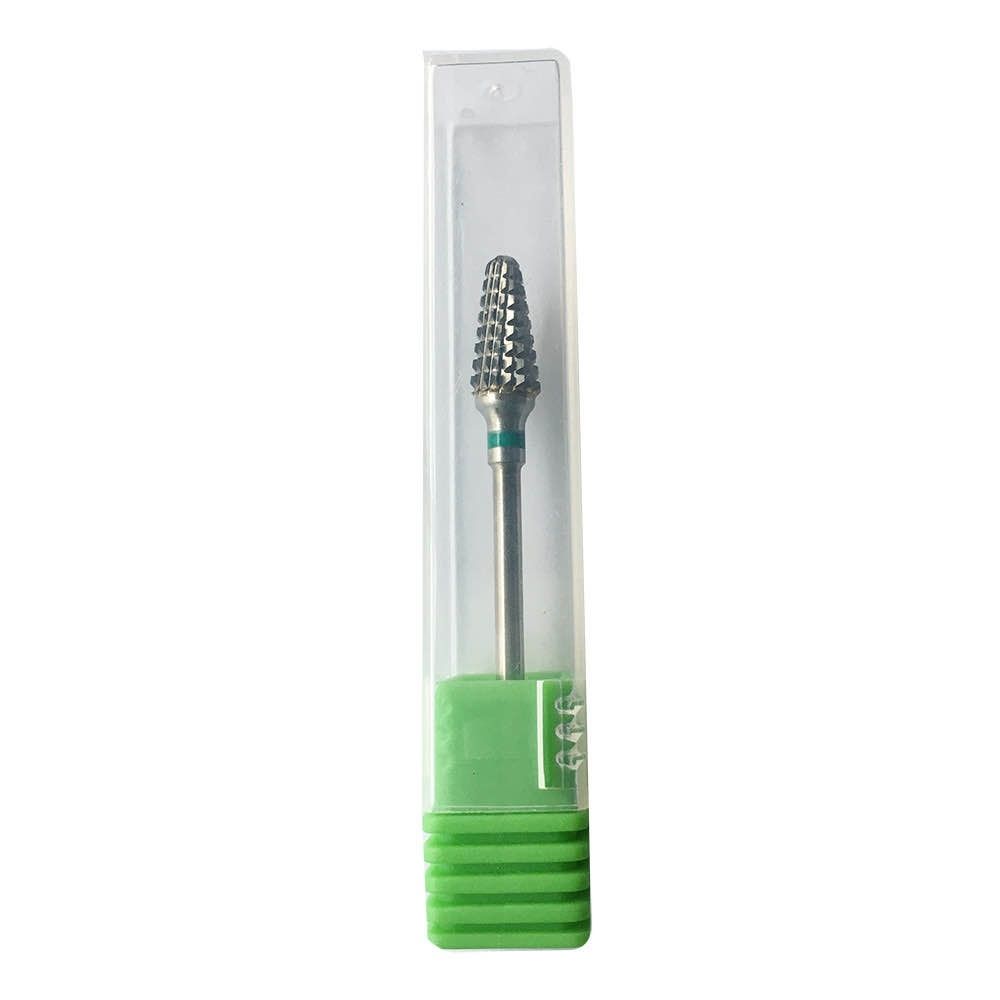



1. Acrylic (PMMA) Work: Coarse Yet Cool
- Best Burs: Tungsten carbide (coarse grit) or ceramic HP burs.
- Tip: Low speed with water cooling to prevent melting.
2. Metal Crown & Bridge: Tough on Alloys
- Best Burs: Tungsten carbide (durability) or HSS (soft metals).
- Tip: Air/water spray reduces heat and tool wear.
3. Zirconia & Lithium Disilicate: Glass-Ceramic Sensitivity
- Best Burs: Diamond burs (resin-bonded for lithium disilicate, silicon rubber for zirconia).
- Tip: Light pressure + cooling prevents cracks and overheating.
Application-Specific Tips
- Trimming & Grooving: Wheel-shaped diamond/carbide burs for even cuts.
- Margin Refinement: Tapered/feather-edge diamond burs for precision.
- Polishing: Composite burs or rubber points for a high-gloss finish.
Key Takeaways
- Match material to bur: Acrylic = carbide/ceramic; metal = carbide/HSS; glass-ceramics = diamonds.
- CAD/CAM vs. Hand Tools: Milling burs prioritize speed, heat resistance, and precision for digital workflows.
- Invest in quality: Durable, material-specific burs save time and cost in the long run.
Looking for dental lab burs? Dental Laboratorio is a reliable place to go. With a curated selection of burs optimized for acrylic, metal, zirconia, lithium disilicate—and specialized CAD/CAM milling tools solutions—you’ll streamline your fabrication process and elevate your restorations. Explore our range today!